from Kroxx@lemm.ee to linux@lemmy.ml on 13 Jan 22:20
https://lemm.ee/post/52533824
I recently took up Bazzite from mint and I love it! After using it for a few days I found out it was an immutable distro, after looking into what that is I thought it was a great idea. I love the idea of getting a fresh image for every update, I think for businesses/ less tech savvy people it adds another layer of protection from self harm because you can’t mess with the root without extra steps.
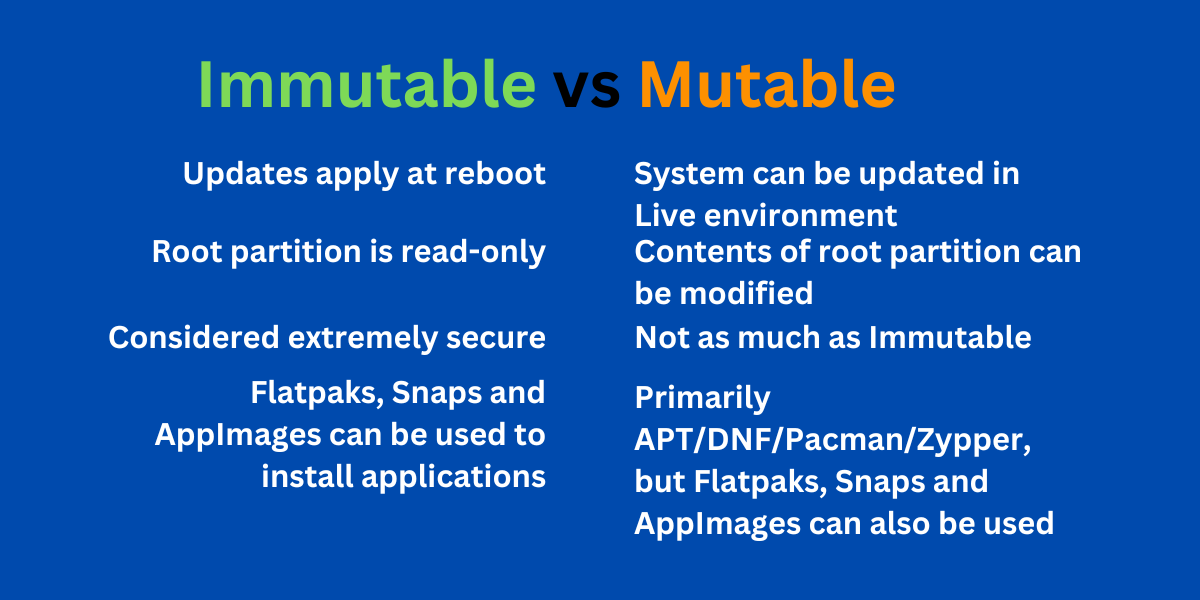
For anyone who isn’t familiar with immutable distros I attached a picture of mutable vs immutable, I don’t want to describe it because I am still learning.
My question is: what does the community think of it?
Do the downsides outweigh the benefits or vice versa?
Could this help Linux reach more mainstream audiences?
Any other input would be appreciated!
threaded - newest
Immutable, doesn’t mean extreme secure. It’s a false sense of security.
It could be more secure.
But during a runtime, it is possible to overwrite operational memory, mask some syscalls, etc.
That’s my 3 cents.
Fully agreed. On almost any atomic distro, /home/user is writeable like usual, so any attacker is able to persist itself by editing
~/.bashrcand putting a binary somewhere.I didn’t know that inflation can affect idiomatic expressions.
it doesn’t allow changes to stuff that needs root access to change. If you have root access you can do anything, including switching images. It is not more secure. It’s not less either
Secure can also mean more resilient. The infosec C-I-A triangle has three legs. Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability. Immutable distros are more resilient and thus offer better availability in the face of attacks or accidents.
–apply-livetag (or however it’s spelled).I run bazzitr and distrobox is amazing. No need to worry about distro when some devs only provides deb only.
Distrobox is something I want to start playing with, I like the idea of the containers
With Aurora, I was unable to get winehq working without installing it from a distrobox instead. I can now play SimTower on my Linux PC.
I really appreciate rarely seeing the message “update complete, please reboot now”. I would consider myself on the tech savvy side though.
Yeah what I really meant was you don’t have to have much linux experience to jump in, I definitely like the idea of not doing live updates now that I know it’s an option
I remain interested in the immutables or atomic distros because I know a lot of smart people that swear by them.
I also don't try them just yet because I know a lot of dumb people like me that end up breaking a lot of stuff before quitting them altogether.
They could be amazing and just not perfected yet or they may be a meme and no one's proved it outright just yet. Will be lurking this thread either way lool :D
Yeah I think atomic is more appropriate but I’m not exactly sure what the difference is?
Immutable = Read-Only Root FS && Updates entire system image rather than individual files
Atomic = Updates as single transaction (all or no update) && Containerization w/ Rollback capability
This is quick summary from quick research pls correct where technically wrong.
That makes sense, bazzite is referred to as atomic (that’s what I meant in the above comment about atomic being more appropriate, forgot to add that context though lol) specifically instead of immutable. Bazzite updates like you said and you can always roll back, thank you for the explanation!
If we’re asking what people mean when they use those descriptors, then you’re correct.
However, literally speaking, in this context, immutable only means read-only, and atomic only means that updates are applied all-at-once or not at all (no weird in-between state if your update crashes halfway through).
The rest of the features (rollbacks, containerization, and immutable meaning full system image updates) are typically implied, but not explicitly part of the definition.
I knew a real wizard would clarify sooner than later. Much obliged and keep up the good work anon!
These distros are great for beginners or less technically savvy. They’re really just harder for people who have been using Linux forever and are very accustomed to the old ways.
I’m using Bluefin and overall it’s great. However, there are some unique issues due to immutability and flatpak.
On Bluefin, I can access my NAS and all files using the Files app, but not using FF, and I cannot accomplish the above task in the same way. Firefox cannot fully access my NAS, and I have not figured out how to make it work. I’ve played around with Flatseal, but no dice. Instead, I need to use Files to download the files from my NAS to a local folder, and then I can use Firefox to upload to PD from that local folder. I’m guessing there is a better way, but I haven’t figured it out yet.
EDIT: This thread motivated me to try and fix this issue. Installing Firefox using rpm-ostree worked. I expected it would, though I am still hoping to figure this out using the Flatpak version at some point. I also tried using Distrobox/Box Buddy to create a Fedora 40 box and install Firefox there. That version of Firefox couldn’t even see my NAS at all (unlike the Flatpak which could see my NAS but couldn’t upload files from the NAS to Proton). This was my first time ever using Distrobox. I thought it was super cool to see it in action and get a working Firefox, even though I couldn’t use it to access my NAS as hoped.
So while most things “just work,” there are some problems. Planning to stick with it and keep learning. I do love the concept and I’m overall very happy with everything.
For #1 could you use distrobox to run it with another OS? I’m pretty new to all this so I could be way out in left field lol.
I haven’t tried any distobox stuff yet but I’m very curious. I will at some point.
Whoever downvoted this is lame. I appreciate your question.
I added this edit above. Pasting here in case you are curious. Cheers.
I use Proton Drive on Librewolf on Bluefin without issues, so that seems a little odd. It might be an issue with what access you’ve given the fkatpak. Flatseal is the right place to look.
Are you using librewolf to upload files from your NAS to Proton Drive?
I readily admit I am still not super proficient with flatseal. I spent a lot of time trying to fix this by adjusting the file permissions, but I’m now wondering if it was some other local network setting I missed.
I also don’t use fstab to mount my NAS. I just sign in using Files which creates a smb link. On Firefox/proton drive website I can see the files but I cannot upload them directly to Proton Drive from my NAS using Firefox (or Zen) on bluefin.
In the Filesystem section for that app in Flatseal, you need to add the path to your NAS drive (the same SMB path that it’s mounted in the Files app). That will give your FF flatpak access to that location.
<img alt="" src="https://lemmy.world/pictrs/image/0bb1cf49-8fa8-4e95-89f2-8f4890c69c00.png">
Thanks. I tried that using:
smb://[NAS NAME].local/[FOLDER NAME]/
I copied that path straight out of the Files app. Unfortunately it does not work. There is a yellow exclamation point flag next to it that says “This is not a valid option.”
I ended up installing the rpm-ostree version of Firefox, which accesses my Nas just fine for proton drive uploads. I do hope to eventually figure out how to do this with flatpak/flatseal, but this works for now at least. I appreciate the help!
<img alt="" src="https://lemmy.world/pictrs/image/fd8ecf4e-56f3-479b-9b61-6b7f6bdf46a6.png">
These seems to be related to flatpak, not immutability.
I agree. I installed the rpm-ostree version of FF and it worked as expected.
More like familiar and unfamiliar
Yeah that’s what they said
The root filesystem is being read from somewhere, and if it’s being read from, it can be written to. Having an extra step or two in the way doesn’t make it “extremely secure”.
Why would being able to read imply being able to write?
Well it can greatly improve security by preventing a compromised app to achieve persistence.
Unless “read-only” is being enforced by hardware (reading from optical media, etc), a compromised sudo user can circumvent anything, and write anywhere. A read-only flag or the root filesystem being mounted from somehwere else are just trivial extra steps in the way.
Improved security != extremely secure, is all I’m saying. There are a lot of things that go into making a system extremely secure, and while an immutable root filesystem may be one of them, it doesn’t do the job all on its own as advertised in this post.
is nixos considered immutable or mutable? kind of has characteristics of both.
nixos and guix are immutable and two of the only immutable distros I like
The store is immutable but the system itself definitely isn’t.
.
Packages in nix are in the store directory, each package in a dir named after the package hash. So you can have 15 versions of firefox installed, for instance, and the different versions go in different folders with different hashnames.
When it’s time to set up a user env, their specific version of firefox is (conceptually) symlinked into the users profile. When that user executes firefox it gets one out of the 15 versions. Another user may get a different one.
Anyway, the package store is off limits to users, and a real bad idea to modify for root too.
.
That’s not what sandboxed means and Nix isn’t sandboxed.
Sandboxed means it runs in a separate container, often with limited permissions; raising security at the cost of performance.
.
What namespace are you talking about?
I’d argue it’s closer to a mutable distro than an immutable one.
Nixos tends to lean on the term reproducible instead of immutable, because you can have settings (e.g files in /etc & ~/.config) changed outside of nix’s purview, it just won’t be reproducible and may be overwritten by nix.
You can build an ‘immutable’ environment on nix, but rather than storing changes as transactions like rpm-ostree, it’ll modify path in /nix/store and symlink it. Sure, you can store the internal representation of those changes in a git repo, but that is not the same thing as the changes themselves; if the nixpkgs implementation of a config option changes, the translation on your machine does too.
Interesting. If possible, could you more explicitly draw comparisons on how this isn’t quite the same over on say Fedora Atomic? Like, sure changes of
/etcare (at least by default) being kept track of. But you indeed can change it.libostreedoesn’t even care what you do in your home folder. Thus, changes to e.g.~/.config(and everything else in/var^[1]^) are kept nowhere else by default./optare actually found here as well.~/.config is probably a poor comparison on my part; it’s management is actually done by home-manager rather than Nixos proper, and I can’t think of another OS that fills this same role.
Nixos generates (for example) /etc/systemd/network to a path in /nix/store and symlinks it to it’s appropriate locations. After the files are generated the appropriate /nix/store paths are (re-mounted? Over-mounted? I’m not sure the implementation) made read-only (by default), but anything that isn’t generated is absolutely both mutable and untracked, and that “not tracking everything in /etc” is more what I’m going on about.
If you use Nixos as intended (when you find that a package is lacking a config option you want, create your own nix option internally) the distro is effectively immutable, but if you use Nixos for anything moderately complex that changes frequently e.g. a desktop os, you eventually run into the choice: become competent enough to basically be a nixpkgs contributor, or abandon absolute immutability.
I think the first option is worth it, and did go down that route, but it is unreasonable to expect the average Linux consumer to do so, and so something like fedora atomic is going to remain more “immutable” for them than nixos.
This need to git gud is thankfully lessening with every commit to nixpkgs, and most people can already get to most places without writing their own set of nix options or learning how to parse //random markup language// into nix, but you’ll eventually run into the barrier.
It’s definitely great for the mainstream. Think of Linus Sebastian who has somehow broken every OS except for SteamOS.
It’s not great for me who uses Arch Linux btw with the expectation that if the system doesn’t break on its own, then I will break it myself.
Honestly, I would say it isn’t great for anyone who has to do something low level even once. Now that there are open source nvidia kernel drivers that has solved a pretty big issue for most people who would be interested in immutable distros, but there are still many other drivers and issues that your regular user may face.
One example off the top of my head is that flatpaks specifically can’t ship systemd services if I recall correctly. A lot of wayland apps for thigns like input have to use daemons because of wayland’s security model. Lact for AMD and now Nvidia GPU control, ydotool, or even gui versions of such tools for remapping input.
Snaps require custom kernel modules that aren’t used outside of ubuntu, so I hesitate to trust them regardless of any of the other issues people have with them.
This basically leaves appimages which aren’t available for everything and don’t always seem to work at least not as reliably as flatpak. I even tried to package the rstudio forensic software as an appimage myself, so I could have an easy way to use that proprietary piece of software, but I just couldn’t get it to work. I couldn’t get it to work with distrobox either using the official methods they provide to install it on linux. I did get it working in a chroot for some reason, but it had graphical issues. In the end, I made a PKGBUILD for arch and got it working that way.
The point of all this is that a lot of times people say immutable is great for average, non tech savvy people, but I believe that literally everybody ends up needing to do low level stuff at least once or twice every so often. Which simply isn’t a great experience since you end up having to do layering which throws these theoretical average users right back into the normal complexity of a mutable system, but with even more uncertainty in my opinion.
Now then with all of these caveats. I do still agree that immutable distros are great for the aforementioned group of people and I know this statement contradicts a lot of what I have described above. The reason why I think they are great for the less tech savvy people however isn’t because of any actual technical merit of the systems design though. Immutable distros are great for people like Linus Sebastion because it limits what they can do. You simply have to accept what is there the same way that you have to on proprietary systems like Mac and Windows. Those systems force you to do things a certain way unlike Linux and that is what people like Linus need because they have no business mucking around with the system to begin with.
Lastly, all of this only works because devices like the Steam Deck are being run on specific hardware thus guaranteeing there compatibility. This is what we ultimately need. There would be much less need for low level operations to get drivers or change settings to make wifi or audio work right on a billion different devices if these people were buying linux compatible hardware in the first place.
You can install packages in immutable distros. It’s just not as easy and recommended as a last resort.
With Universal Blue (Bazzite, Bluefin, Aurora) you can install packages with “layering”. It’s basically modifying the image by adding packages on top of what is shipped by the distro, and those packages get added each time the image is updated.
The better, more involved solution is to create your own image from the base image. That gives you a lot more control. You can even remove packages from the base image.
Weird, I don’t have any issues developing custom systemd services or similar on my Kinoite installation. Packages that need to run on the host system can be layered, everything else is running in distrobox.
These are valid concerns but to me they sound more like lack of tooling rather than inherent disadvantages of immutable distros. Linux distros have not historically been designed from the ground up for immutability and it makes sense that there are issues that aren’t handled optimally. Surely we can come up with clean and simple solutions to basic problems like setting up daemons and drivers if we work on it!
And anybody who thinks that Linus doesn’t look for those ways to break Linux is deluding themselves. He’s a fucking asshole.
He can be an asshole, but I believe finding bugs is part of his job.
Would you rather have him find them and complain to a community who might know what they could be, or someone else who will just complain and buy a MacBook instead?
I used an immutable fedora on my surface pro 4, I wanted to shoot myself in the face every time I had to install anything. I’m good on that for the rest of my natural life.
Was what you wanted not available in a flatpack/ app image?
Wasn’t about that at all. Any DNF action took a lightyear… man just typing out those long commands (very hard to remember coming from apt) nevermind the much crazier wait time. Using toolbox for dev environments to compile things was a total nightmare. I’m sure there’s a scenario where it’s ideal, that was certainly not my situation.
Gotcha I was just wondering what the limitations are, I’m still messing with and I’ve not hit one yet but I was curious where they pop up. So for devs immutable distros don’t play well, that definitely makes sense!
From what I gather, if you like tinkering and compiling and installing random weird apps then immutable can be a serious pain in the ass like I discovered.
Did you ever try using Distrobox? That’s the recommended way if installing random apps.
I’m not sure that would’ve influenced my situation with a dual core i5-6300U and 4gb ram, it’s a pretty sluggish thing from the get go. But good to know about distrobox maybe that can help me in the future. Now rocking Debian and it’s great.
Debian sounds like a great fit for you. But it’s good to know that Universal Blue has a lot of tools available for installing and tinkering that many just don’t know about. They are extremely powerful OSs.
I think it’s good if you have a ton of storage and want to set it and forget it. For me, immutable depresses me. I came to Linux for the tinkering and the ability to do what I please to my system, not to be restricted. That’s just me, though. For handhelds/strictly gaming machine (a Steam machine for example)? I think immutable is the perfect fit for it.
Do you have any examples of the kind of “tinkering” you couldn’t do with an immutable distro? I haven’t run into any restrictions after more than a year.
You can’t even install packages using sudo. You can, but they’ll be overridden on next update.
… why would you want to install packages with
sudo? The proper way is to install them (as a user, not root) usingrpm-ostree, which will layer the packages on top of the image, automatically installing them for every future system as well.You haven’t actually looked into immutable distributions, have you?
I admit that I didn’t know about how rpm-ostree is capable of what you mentioned, but I still don’t like immutables for the other reasons I’ve mentioned. I did look into them and I can’t use them. I like my regular distro
I keep hearing this, but people never elaborate on those “other reasons”. Did I miss where you mentioned them?
You mentioned storage, but AFAIK atomic Fedora doesn’t use more space (unless you keep multiple versions for rolling back).
I don’t want to deal with images. I don’t want to have to be cleaning the system from those images to reclaim my storage. I dislike flatpaks, snaps and appimage on which immutable distros rely. The lack of customization as you can’t modify system files or install traditional packages outside the immutable framework, which limits personal tweaks. Apps availability, not all apps on the planet exist in flatpaks. The learning curve. Having to change the way I interact with my computer completely, I’m too fucking lazy for that and way too cozy where I am. They’re just a burden that I don’t want to deal with and I hope that that’s ok with you. Lmao
Of course it’s ok! You do whatever you want. Though I’d like to clear up a couple of misconceptions:
You don’t have to, happens automatically.
Fair, though you don’t have to use them at all - you could run everything in a distrobox.
This really depends on what system files you mean. Anything in
/etc/? Fully writable. Everything is configurable either in your home directory or in/etc/, so I haven’t run into any issues with not being able to modify something - and if you do run into that, you always have distrobox.Don’t need to, you have distrobox for that.
That’s fair. It’s been very small for me, and the issues have helped me become a better Linux developer, but it does bring its own problems in some cases.
That’s the thing, I hear this a lot, and I just don’t know what the big changes are. I installed Kinoite, set up a distrobox, and have been smooth sailing since - all my previous installations have had far more issues, and I just haven’t really changed much (besides switching from Ubuntu to Fedora, but I’m happy about that, fuck Canonical).
See, most of those things you mentioned are new things that I have no interest in getting into. I don’t know how to explain it, but the fact that you started listing ways to fix the things that are totally avoidable by me and I don’t need to bother with because what I have works fine, is an instant turn off. I’ve messed with distrobox and I hated it, just like how I hated nixOS. It’s just not for me. I can’t get into it even if I tired. Distrobox is just another thing I don’t need nor want to fuck with, because, again, what I have works perfectly for me. It’s different from person to another. You might like to dig into new things, but I don’t. I do other things on my machine. I have one workflow and I’d quite literally get into depression if I changed it, no joke. I like to set things one way and keep that one way forever. I’ve been running Linux since 2018 and have always used Plasma, and have always used it on an Arch based distros(never Arch itself surprisingly). I have had the same set up all these years. I’ve tried gnome for a while and I literally hated my machine (no disrespect to any gnome user or the gnome team). I hope that makes sense. I get that you defend/advertise/make look good the thing you use. It’s an internal justification, I get it, but people have different likes and dislikes.
All that’s totally fine! I wasn’t trying to convince you. I just don’t want newbies to get discouraged by reading “all this stuff is non-standard and you can’t tinker and do stuff”. Because you can, it’s the same stuff.
Newbies should have no business messing with stuff like this to begin with. They should start with mint and call it a day. Lol
Definitely not, this kind of system is perfect for newbies. You have a distrobox you can break all day long, and your main system stays nice and working.
That’s what I mean. You put it like it’s incredibly complicated and strange, when there’s pretty much only upsides. Do you have any idea how much time I’ve spent on various distributions to debug NVidia issues? Everything is working perfectly now, and it has for months. I’ve never had this good of a Linux experience.
I’m not really sure how the upsides of immutable distros work. I’ve been using linux for a long time and I’m not an expert but I’ve learned bits of things here and there.
I recently bought a steamdeck and it’s running an immutable distro. I don’t really know how to use software that’s installed via flatpak because it’s weird.
I have a game installed that runs badly (unplayable for me) through proton. I can launch it through q4wine if I switch the steamdeck into “desktop mode” and it runs much better.
If it wasn’t an immutable distro I could pretty easily make a shell script that launches the game through wine. Then I could add that shell script as a non steam game and it would (I think) run well, and I’d be able to launch it from the non desktop side of steam OS that is a lot more streamlined.
There is something comforting to me about immutable distros though.
I feel like I don’t remember half the shit I have installed on my computers. If I wanted to start cutting things out I don’t know where I’d start. But with flatpaks I get the sense I could probably just wipe anything I don’t use out of the flatpak directory and I probably wouldn’t break anything.
I’m fairly certain you could still run that shell script on steamOS? I don’t understand why an immutable distro would keep you from doing that. It’s essentially what Lutris and Heroic Games launcher do.
N I x o s
.
Atomic and declarative. Which is way cooler.
Solves the issue tho
Well it’s a bit confusing. On Guix’ wiki General features you can read:
And then on its wiki Guix System (operating system) Roll-back you can read:
So the system configurations on a Guix system are actually immutable, as opposed to regular gnu+linux distributions, which can change the system configuration on the fly. What else is immutable on Guix, I can’t tell, but at least you can not change its system configs. What is atomic is the upgrades.
I’m not sure, but as Guix borrowed these properties from Nix, I’d think this applies to Nix as well.
In other words, at least the Guix system has immutable components. And further, the system config which is immutable, is also declarative. Combining those two things might be intimidating, since it’s not like on the fly one can go and change the system config, which might be required when debugging some misbehavior, and it’s what most distros document, then one needs to learn about guile, and a bit about functional programming I guess or at least their basics… Deploying systems might take advantage of such declarative configurations though…
Secure != stable Immutable distros aren’t always more secure but rather more stable and hard to break Also btw nixos can apply updates without rebooting
I wouldn’t call NixOS immutable.
In your opinion, when can we refer to a distro as being immutable? How do you regard the likes of Fedora Atomic, openSUSE Aeon or Vanilla OS? Are any of these immutable in your opinion?
To be honest I don’t know these very well. I only use NixOS. My understanding is that in an immutable distribution the root filesystem is read-only. Granted in NixOS the nix store is immutable and most things in the root filesystem are just links to the nix store, but the root filesystem itself is not read-only.
It can be made to be by pinning various things which are not by default.
What things?
At the surface, you can pin the commit you pull packages from, but if you want to go deeper, you can essentially define your own channel and dependent binaries, allowing you to store every aspect of how a generation is built.
Yes, or use flakes which gives you a lockfile pinning everything. But this is related to reproducibility, not immutability.
If you control everything in the build it is, and every generation is immutable.
Isn’t immutability related to the root filesystem being read-only? I can write on my root filesystem, even if it’s mostly links to the store I can replace those links.
I guess that’s true, tbh the reproducibility aspect is really what I like about nix, and I guess I’m confusing a bit here. I guess I’m saying nix gives a good compromise with immutable generations and high repro, but you’ve convinced me it’s not immutable per-se.
Well in the end I think I’m needlessly nitpicking. It doesn’t matter if it’s strictly immutable or not. What matter is that it has the good parts of reproducibility, immutability and declarativity.
NixOS is immutable and atomic, but it isn’t image-based.
Immutable simply refers to how the running system configuration can’t be changed by simply putting a file somewhere (e.g. copy a binary to
/bin, which is a bad idea).For example, Fedora Atomic and derivatives are image based, although they are more flexible than the A/B types like SteamOS.
OpenSUSE MicroOS uses btrfs snapshots to apply updates atomically, and is more flexible than most image based immutable distros.
Edit: But I don’t think those terms have a single definition, so how would you differentiate these terms?
<img alt="" src="https://jlai.lu/pictrs/image/5d6d52cd-8393-48e9-a2cf-81586fa9fc8e.png">
I’m on NixOS right now and just dropped a Chewy in my
/bin, only had tosudo touch /bin/chewy.Good point. I’ll have to stop using immutable and stay with atomic (and declarative).
Interestingly
/binand/usr/binare not in PATH by default, so/bin/chewycan only be executed by its path directly and won’t affect the systems reliability.That doesn’t make it not immutable. /bin is not a critical directory in NixOS, only the contents of /nix are, which are immutable. /bin isn’t even part of your path by default.
Well that was an approximation to keep it simple and disprove the given example. There are other directories in the root filesystem that are in the path by default, or used in some other critical way (like
/etc). Even if they are links to directories in the nix store you can replace the link.I understand, but it didn’t really disprove anything. Immutable distro’s protect core components from being modified. /bin is hardly relevant on NixOS, so of course it wouldn’t be made immutable.
/etcis also generally not considered a core component, and every immutable distro I’ve used left it writable. By default, every binary installed through NixOS is put in/run/current-system/sw/bin, which is immutable. Many other important files are also linked to/run/current-system, which is why the whole directory is immutable. It essentially takes the place of what the root directories would be on an FHS distro.I don’t know any other path used in critical ways that is not immutable. The primary paths that immutablility is relevant for in FHS distros are /usr, /lib, /lib64, and /bin. None of these paths are really used on NixOS, besides some files symlinked there for edge cases, like /bin/sh.
If you were to remove all the symlinks you are able to, the system would still work for the most part. You would lose custom configurations in /etc, but that is true for most immutable distros. Most apps have a default configuration to fallback to.
The misunderstanding comes from the fact that immutable is a poor description for any OS, which is why many now use atomic instead. Even in immutable distros, many files can still be modified, and things can still be broken if you try hard enough. Still, NixOS definitely falls under the general description of and immutable distro, as the core of the OS is immutable.
As someone who hasn’t looking into nixOS much, I feel like I had a stroke reading your comment lol
I’ve used Bazzite for the last year or so after distrohopping for a while and landing on Arch. I learned how ‘atomic’ distros, as the Fedora folks call them, work. It sounded like my phone, where apps are relatively sandboxed and automatically update. I said ‘this is how computers should work’ and stuck to it.
I wouldn’t use standard Silverblue/Kinoite or standard Fedora. The uBlue images include so many drivers and fixes on the image that make the primary distros look incompetently made if you’re not a power user. They wouldn’t like me saying that because their work is only possible because of what Fedora does. But by that I mean, you will eventually run into something that doesn’t work and it always comes down to some licensing or scope issue that the developers simply don’t care about.
Having to do literally anything extra to get your NVIDIA GPU drivers frankly isn’t acceptable when that’s not the case for AMD cards. Let alone having to modify grub in the worst case if your distro doesn’t boot properly. If I have a part or plug something in that isn’t some hyper specific piece of technology, it should just work, because it isn’t 1999 where you need driver CDs anymore.
The main tradeoff is that for users who aren’t very technical, installing anything outside of flatpaks probably won’t make any sense. They have guides, and stuff like brew and distrobox isn’t that difficult when you understand it. But having 4 different ways to install stuff (flatpak, brew, distrobox, layering) sounds ridiculous and confusing on its face.
I have a practically 0 maintenance system with Bazzite and that’s the way I like it even though I’m perfectly capable of running anything else and modifying it to my liking. The average user isn’t going to care about anything they’re missing by not being able to modify certain files, or if they do, there’s probably a better way to do whatever it is they’re trying to do that doesn’t involve running random bash scripts.
I would recommend Aurora and Bluefin to all my Windows/Mac friends who aren’t gamers, and Bazzite or Bazzite-gnome to everyone who is. I would never recommend anything else at this point, not even something like Mint, because I consider the uBlue images to be just that good and the tradeoffs of the weird program installation to be more than worth it. Other immutable/atomic distros are too immature (like Arkane Linux) or work fundamentally differently to Fedora Atomic and rely more on things like snapshots (like OpenSUSE Aeon/Kalpa) so I’m not really comfortable recommending them either.
Has anyone had good success with setting up a development environment in an immutable distro? I love the entire concept because it fits with a lot of my other software preferences, but the tools for containerized dev environments felt frustrating.
Like, what do you do for your editor? vscode + devcontainers feel like the best option, but it’s rough when I need other IDEs (like I use some of the Jetbrains products). Stuff like toolbox works well too, but to get an editor in that, you have to install it in each one, or make a container that has it built in.
Otherwise, I’ll stick with plain Fedora — I use flatpaks for all of my apps anyways (except my editor)
I do my main development with Bazzite. I use the Neovim flatpak for my editor and toolbox for builds and such.
Running cli apps like neo vim from a flatpak is frustrating… “flatpak run com.something.neovim” is just the worst way to handle things. Complete deal breaker.
Why is it a bad way to handle things?
I have an alias set up and SDKs enabled. The experience is indistinguishable from a regular install. But you could also layer it onto the os image or install it in user space if you don’t like flatpaks for the extra resource usage or something. That’s a complete non issue for me though.
That’s not indistinguishable - that’s you working around the problem of running
flatpak run some.domain.IForget(which - BONUS is case sensitive which is awesome) to run neovim.Snaps install a binary you can run. Flatpaks make you remember the 3 part domain to run things. So you setup aliases after installing things to run them, and if you uninstall them you need to remove your aliases. It’s a complete own-goal by the flatpak developers that this mess exists and is completely unnecessary. Simply providing an option to create and manage a script in .local/bin or something would be all it takes to make flatpaks usable from the CLI in a way that isn’t obnoxious.
That’s a good point. I should have said “indistinguishable after some tinkering”. You raise a valid complaint, though it’s not a deal breaker for me.
Personally, I have found the developer experience on Bluefin-dx (the only one I’ve tried…) to be…. mixed.
VSCode + Devcontainers, which are the recommended path, are pretty fiddly. I have spent as much time trying to get them to behave themselves as I have actually writing code.
Personally, I’ve resorted to using Homebrew to install dev tools. The CLI tools it installs are sandboxed to the user’s home directory and they have everything.
It’s not containers - I deploy stuff in containers all the time. But, at least right now, the tooling to actually develop inside containers is kind of awkward. Or at least that’s been my experience so far.
I think the ublue project is fantastic and I really like what they are doing. But most of the world of developer tooling just isn’t there yet. Everything you can think of has instructions on how to get it going in Ubuntu in a traditional installation. We just aren’t there yet with things like Devcontainers.
Using brew is the recommended method on uBlue, so you’re already doing the right thing.
That being said, I use Jetbrains and devcontainers on Bluefin-DX and it’s been flawless for me, straight out of the box.
Hmmm, interesting. I like brew, for sure. And devcontainers worked ok for me when I was working on something by myself.
But as soon as I started working on a side project with a friend, who uses Ubuntu and was not trying to develop inside a container, things got more complicated and I decided to just use brew instead. I’m sure I could have figured it out, but we are both working full time and have families and are just doing this for fun. I didn’t want to hold us up!
Our little project’s back end runs in a docker compose with a Postgres instance. It’s no problem to run it like that for testing.
Maybe a re-read of the documentation for devcontainers would help…
I use Jetbrains, devcontainers, and distrobox on Bluefin-DX and it has been flawless out of the box. There’s a single command to install the Jetbrains toolbox, which let’s you then manage all their apps.
Couldn’t recommend it enough, made my development lifecycle so easy.
How do you use the Jetbrains tools with distrobox? So far I’ve manually installed the toolbox inside my distrobox, but that doesn’t seem to be the preferred approach.
No need for distrobox for that - it’s a built-in
ujustcommand, put there by the creators of uBlue. It really has everything you need out of the box.More info in the docs: docs.projectbluefin.io/bluefin-dx#jetbrains
Yes, I got that running - but how do I then allow the Jetbrains tools to use CLI tools in the distrobox?
For distrobox, you can export your CLI tools, then use them anywhere in your system:
Alternatively you could
distrobox enterfrom the Jetbrains terminal.I would generally use
brewfor installing system-wide CLI tools, and use a devcontainer if I want to have a specific dev environment for a project.i started learning rust with nixos, you can declare a shell.nix with everything needed for the environment, and those things will only be available in that folder.
there are caveats and annoyances to this like building a python environment costed me some time, because python packages sometimes require compling and all the shared libraries in nix are not in the right path (because you can have multiple versions installed) so you need to set some env vars to patch this.
nothing that gpt cannot solve.
I need to run immutable distros more, and I need to figure out how to roll my own images.
Desktop side, I need certain things in the base image rather than adding more layers or using a container. Things like rsync, nvim, git, curl, lynx, etc.
Would immutable distros help reach more desktop audiences? Perhaps. It’s more about applications though. The biggest help has been electron apps and the migration to web apps. The Steam Deck is successful because it has applications people want.
Server side, they look really promising for bare metal servers. Provided, there is an easy way to compile custom images. Being able to easily rollback to a known good image is very enticing, as you point out.
I am a big fan of breaking my system
Stock fedora is just for you my man, it breaks by itself
arch >>>>
Arch doesn’t break by itself tho, well… If you don’t update it for few months then yes, it breaks by itself
Exactly. Arch is just better for the user to break. I like to break my system, not the system breaking by itself.
Manjaro enters the room…
I don’t mind flatpaks, but overall I don’t enjoy how software installs on immutable distros if it’s not flatpacked. It’s quite a kludge.
It’s subjective. I freaking love Bazzite, it works for me. Not the other way around.
Feel like elaborating? I’ve been running it for a couple weeks and very happy so far. One nice little feature was how I can just scroll on top of the little sun icon in the taskbar and my monitors dim and brighten. But that’s prolly a Plasma thing more than anything else.
That’s indeed a Plasma thing
I had to turn it off (which is easy in plasma) because I have two different monitors and they have different brightness, so it was either first one insanely bright to other one being normal or first being normal to second barely dim.
I use plasma and had no idea this was a thing. Thank you
My new measure for intuitiveness of an interface - do half-drunk, clumsy fumblings with a mouse occasionally reveal a slick new feature I wasn’t aware of?
One thing I really like about Bazzite (compared to EndeavourOS which I ran before), is that it just works for gaming. Lots of little tweaks and stuff to get certain qol things working in EOS, are just installed and configured by default in Bazzite.
The stability is super impressive… I used to rely on TimeShift on EOS to roll back when I broke shit (which was over and over, because that’s how I learn), and while it’s trivial to rollback on Bazzite, I’ve never even been close to needing to. It’s just hard to break (and if you do, just reboot it and everything is fine).
It’s definitely more user friendly, but I wouldn’t say immutable like Bazzite is only for non-tech people.
Thanks for the info! So far I’ve been enjoying those same characteristics. I spend my work day arguing with computers, so I have little patience for doing more of it when I’m off (more seriously, I carefully marshall my tech efforts outside of work as a long-term strategy against burnout). I appreciate how “out of the box” gaming (and anything else I’ve tried) works in Bazzite, and the stability has been great too. Though to be fair, def helps that it’s my first experience with Plasma which really makes the “feeling” of the OS pop, in an unfair way lol.
Plasma is awesome! The customizability is just off the charts.
Yesterday I powered up my older laptop (running EndeavourOS) after not starting it up in several months. Had to install the updates in chunks because there were just too many, and the dependency situation was a nightmare… Anyway, got it all updated.
and then next thing I know, I look at the clock and like 3 hours passed. I had been tinkering with shit, completely unnecessarily, for hours without realizing it. I don’t think I really accomplished anything, and in fact may have left it worse off than it was before I turned it on lol.
So yeah, TONS of time saved using Bazzite, but there is that level of tinkering that I do miss at times (DistroBox can help with some things). I don’t even know if I’d say it’s something I “enjoy,” per-se… It just tickles my brain in a certain way that I don’t get elsewhere?
NixOS is kinda the best of both worlds, because it does everything in a way that is compatible with an immutable fs, but it doesn’t force you into abiding by immutability yourself.
You can always opt into immutability by using Impermanence, but I’ve never seen any reason to.
Edit: That said, the syntax has a steep learning curve and there are tons of annoying edge cases that spawn out of the measures it takes to properly isolate things. It can be a lot to micromanage, so if you’d rather just use your system more than tinker with it, it may not be a good fit.
Impermenance is not the same as immutability.
I suppose you’re right. It’s just another tool for helping you abide by immutable practices without forcing immutability as an unbreakable rule.
I switched to silver blue after a bad update and my experience has been almost identical if not smoother than standard fedora
TL;DR: My desktop PC uses EndeavourOS and the only immutable experience I have is SteamOS 3. I can’t say one approach is better than the other, but I like having the newest software and packages in my system. And that’s best provided with a rolling release. I also think that sandbox systems like Flatpak and the several alternative installation methods besides the system package manager is an added complexity for a new user in Linux.
I don’t mind using an immutable system (BTW another term that describes this kind of system is Atomic, which comes from Fedora), as long as it is designed around it and works well. The only immutable system I use is on my Steam Deck with the pre-installed SteamOS 3. My generic desktop personal computer is using an Archlinux derivative EndeavourOS with a rolling-release, where I have much greater control over the system.
Both systems have their strengths. I don’t think that my mutable and always up to date system is breaking more often than the other system. The best part of it is, its always up to date and I get the newest applications. I try to not use much Flatpaks or AppImages (but do for certain apps, where I have no other choice for ease of use). And an immutable system naturally basically asks me to use Flatpaks and other user space package formats that is not handled by the distribution itself.
Even though I have some thoughts on it, I am not excluding one approach. Many say that immutable distributions are good for new users to Linux. I think this adds some complexity and problems, because they need to use sandbox systems like Flatpak. And that’s if they know that they are using Flatpak, because sometimes the app distribution gives options like AppImage and custom installer scripts as well. This is all confusing for someone who just starts with Linux. On top of it, the sandbox of Flatpak requires some additional setup and configuration for some apps, to access certain hardware or filesystems in example.
All in all, I tend to like the traditional “mutable” distribution system as a rolling release model the most. But I’m an not excluding any other and would use a good “immutable” one; I just didn’t try any other than the one in my Steam Deck.
It’s important to note how the Linux community interacts with change. In the past, whenever a change has been significant enough to influence individual workflows, it often provoked strong reactions. This was evident when systemd was introduced and adopted by distros like Arch and Debian. Even though systemd was arguably superior in essential aspects for most users, it failed to meet the needs of at least a vocal minority. Consequently, community endeavors were set up to enable the use of Debian or Arch without systemd.
Similarly, the introduction of immutable distributions seems to upset some people, though (at least to me) it’s unjustified. Immutable distributions don’t necessarily alter the traditional model. For instance, the existence of Fedora Silverblue doesn’t impose changes on traditional Fedora; let alone Arch or Debian.
But, overall, most Linux users aren’t bothered by it. Though, they often don’t see a use for themselves. Personally, I attribute this at least in part to existing misconceptions and misinformation on the subject matter. Though, still, a minority^[1]^ (at best ~10%) actually prefers and uses ‘immutable’ distros.
Depends entirely on what you want out of your system. For me, they absolutely do. But it’s important to note that the most important thing they impose on the user is the paradigm shift that comes with going ‘immutable’. And this is actually what traditional Linux users are most bothered by. But if you’re unfamiliar with Linux conventions, then you probably won’t even notice.
As a side note, it’s perhaps important to note that the similarities between traditional distros are greater than the similarities between immutable distros. Also, Fedora Atomic is much more like traditional Fedora than it is similar to, say, openSUSE Aeon or Vanilla OS. Grouping them together as if they are a cohesive group with very similar attributes is misleading. Of course, they share a few traits, but overall, the differences are far more pronounced.
Therefore, it is a false dichotomy to simply label them as traditional distros versus immutable distros. Beyond these names, which we have assigned to them, these labels don’t actually adequately explain how these systems work, how they interact, how their immutability is achieved (if at all), what underlying technologies they use, or how they manage user interactions. The implications of the above. Etc.
The success of the Steam Deck and its SteamOS are the most striking and clear proof of this. So, yes. Absolutely.
Immutable ≠ atomic
Bazzite is atomic (not immutable), same with Silverblue and other Fedora variants (they’re all atomic, even on their main page it says atomic). It’s kinda misleading ngl
Isn’t that just their nomenclature for immutable?
What’s the difference between an atomic distro and an immutable one?
A distro can be both atomic and immutable, and they often go hand in hand.
Immutable simply means the core of a distro is read-only, meaning it cannot be modified by usual means. There are still ways to modify these files, but it works differently than in other distros.
Atomic distros are ones that update atomically. Atomic is used to describe an operation that cannot be cancelled in the middle of it, they either complete, or nothing changes. This means you can’t break things by cancelling an update midway through. Atomic distros also often come with the ability to rollback to the previous build of the system.
Doesn’t all immutable distros have updates that can’t be cancelled and that will either complete or not change anything?
I only just started learning about immutable distros so I may be completely wrong but it’s how I understand them to work when reading about it.
Fedora Atomic IS immutable. Rpm-ostree just layers (or hides) stuff on top of the already existing image. If you layer something, e.g. Nvidia drivers, you still download the same image everyone else uses, but basically compile the driver from fresh and put it on top. And that takes time. This is the reason using rpm-ostree to layer stuff is not recommended.
That’s why uBlue exists for example. It gives you a sane start setup, where all drivers are already built in into the image. And then you can either use the clean base and add your own stuff to create your own image, or use already great ones like Bluefin or Bazzite, where everything you want is already included.
Atomic just means that every process is either completed without errors, or not at all. This way, you don’t get an half updated and broken system for example in case you loose power. Happened to me quite a few times already, but never with Fedora Atomic.
Pretty much anything outside of
/var/(even/home/is placed inside/var/) is read-only, and if you want to modify your install, you have to build your own image. Therefore, it is both immutable AND atomic.That’s why I prefer the term “image based”
Immutable ≠ atomic, but they generally come as a package deal. Bazzite, Silverblue, and all those other distro’s that call themselves atomic are also immutable. An atomic distro is just one with atomic updates, and an immutable distro is any distro with a read-only core.
These distro’s have started mainly calling themselves atomic because they agree that immutable is a poor description that generally confuses users.
Former OS security guy. Fuck no. Nope nope nope nope.
Yes, who would want sandboxed apps which restrict the app’s access to the system. /s
I can see why it’s “former”.
How come?
I can see where you’re coming from because of outdated libraries and flatpak sandboxing not really being a thing (it’s an illusion, really) but you can’t deny that this is the direction we’re moving in, and we need to get flatpak sandboxing and permissions right, to ensure a proper base level of security.
For those unaware:
Many flatpaks use older, outdated, or end-of-life libraries
Flatpak permissions are messed up because most applications ask to bypass the sandbox at install-time
You’re definitely out of date on your knowledge then. Nothing inherently insecure about any of these. Only download software you trust, just like you should be doing with any software format!
If you trust it, why not just install it like a y other app?
Oh wait, it’s generally pushed for binary only blobs, no source… so why are you even trusting it?
I don’t really know what you’re saying. Most software is distributed as binaries, that doesn’t make them inherently untrustworthy, you just need to have trust in whoever is distributing it. It’s trivial to look at the build process of a flatpak and verify that it is legitimate. Just because the binary isn’t being built from source by every user doesn’t make it insecure.
Who is mostly pushing these containerized apps?
Proprietary software vendors.
Same for who stands the most to benefit from immutable distros. Like Android and MacOS get shipped.
Flatpak is completely open source software and any proprietary software in it has a large warning about how it’s proprietary. I don’t know why you think proprietary software vendors are pushing these. Ublue, NixOS, and Fedora Silverblue are all community run, not being pushed by some malicious group pushing proprietary software.
Why companies even have anything to gain from their proprietary software being in a container? All that would do is make data collection more difficult.
Why do you think all phone makers push it?
There is literally no arguing with people like you, haha
So, you cannot or will not answer. Got it.
Go back and look at all the good faith replies to you, and notice that you haven’t replied in kind. You seem like you have a strong and incorrect agenda to push, without being willing to take on any new information which people are providing to you.
You only harm yourself by being fixed in your mindset. There is a very strong correlation between success and people who are able to take on information and grow.
Because it improves security and privacy, something they can advertise as a feature. There’s no negative for them to implement, it’s their phone, they can already collect all the data they want. It still prevents other apps from accessing data they shouldn’t.
Why do you think phone makers push it? What possible malicious reason do you think proprietary software makers have to push containerization and sandboxing? What do they gain?
Correct about security. Unable to inspect the code running, unable to control your own device fully, and really secure at keeping the user out of their hardware.
And for apps shipped in containers? No need to be a part of the FLOSS community, because you can easily ship software to your users that provides no freedoms.
Those things have nothing to do with containerization. They can do those things without it. Containerization exists to improve privacy and security. It can do the same thing on Linux.
Even if you trust an app, it can have vulnerabilities you are unaware of. Containerization helps limit the effects damage from a vulnerability could have. They also simplify the distribution of software, which is the primary goal of Flatpak. There are benefits for using containers for open source software, you’re just refusing to acknowledge them. Nobody is forcing you to use containerization, and I don’t care to convince you to. I just think acting like Flatpak and other container based package formats is some corporate conspiracy is silly. Flatpak is FOSS and mainly distributes FOSS.
I think they’re great. I’ve got two Linux newbies running some Ublue variant with no issues
I personally vastly prefer mutable distros for my own system, but I understand the appeal for those who like them. As long as mutable distros remain an option I don’t mind immutable distros.
Precisely this, linux is about choice. It’s not like suddenly most distros would change init systems and make it near impossible to choose… oh, wait…
I prefer mutable and see immutable mostly as lazyness but if people wanna use’em go for it, i’m not pushing mutable down their throats.
Linux isn’t about choice, it’s about freedom. Distro’s don’t owe you the choices you want, because the devs have the freedom to make what they want. You also have the freedom to modify them or make whatever distro you want.
Immutable distros are great for applications where you want uniformity for users and protections against users who are a little too curious for their own good.
SteamOS is a perfect use case. You don’t want users easily running scripts on their Steam Decks to install god knows what and potentially wreck their systems, then come to Valve looking for a fix.
Immutable distros solve that issue. Patches and updates for the OS roll out onto effectively identical systems, and if something does break, the update will fail instead of the system. So users will still have a fully functional Steam Deck.
If you’re not very technical, or you aren’t a power user and packaged apps like Flatpaks are available for all your software, then go for it. I prefer to tinker under the hood with my computers, but I also understand and except the risk that creates.
Immutable distros are a valuable part of a larger, vibrant Linux ecosystem IMO.
So Bazzite basically is an immutable 3rd-party SteamOS. It was originally designed for handhelds (though has desktop images now) and includes the Steam Deck’s
gamemodepackage. That means it has the same interface, but working on a Legion Go or an Ally X. If anyone here has* any of those three you should seriously check it out!The other thing as well is that more often than not, the update will succeed and you won’t figure out until the next boot that something is wrong. However, Bazzite has a rollback tool so you can just change back to the previous image, reboot again and get to gaming.
That’s the best reason for immutable for gaming IMO. I don’t want to be fucking around with the OS when I’m in the mood to game. Being able to quickly rollback and jump into things in ~10 minutes or less is how it should be.
Immutable are the ultimate tinkerer’s distros. It’s just a different way of tinkering. True tinkering in immutable means creating your own image from the base image and that allows you to add or remove packages, change configs, services, etc.
Example: you create your own image. You decide you want to try something, but you’re being cautious. So you create a new image based on your first with your changes. You try it out and you don’t like it or it doesn’t work for some reason, you can just revert back to you other image.
Another thing worth mentioning, with these distros, you can switch between images at will. I’m new to Linux as my daily driver desktop OS, and I’ve rebased three times. It’s really cool to be able to do that.
Don’t know why this would be downvoted. Atomic distro’s are a tinkerers paradise, as all of it can be done fearlessly. I can make stupid changes to configurations that I don’t understand on NixOS, then when things break, simply revert the git commit and rebuild. (Or reboot to the last build if I broke it bad enough).
Who knows. People are passionate about Linux. And downvoting takes no effort. And people downvote stuff randomly.
if something makes linux more secure, safer or easier to use then it’ll be hated because people in the linux community are allergic to all those things. Secure boot? they hate it, wayland? they hate it, immutability? they hate it, flatpaks/sandboxed app? they hate it, gnome? they hate it. Even rust is hated by many.
I love building my own uBlue image. Tinkering is done in toolbox containers, definite changes are baked into the image. Completely custom (to me) and when you get it right it will just work anywhere. If I would brick my PC/storage I can just boot up another and restore my (back-upped) home dir with very little effort.
I wonder if you can download Apparmor and Apparmor-d on mutable distros, But I faced issues of bwrap and I couldn’t find a SELinux equivalent for Apparmor-d i tried allowing Bwrap but it didnt work so i uninstalled Apparmor.
For my needs, I’ve build a static system with buildroot for a pi zero. No updates, no modifications on the system, no remote access. Some directories are in tempfs, and after a reboot the system is fresh again. when needed, I removed the sd card and copy a new image
I use this board for a pulseaudio/mpd player, it’s not intended for a desktop usage, but I’m happy beiing able to configure a system like this one. For me, there is no maintenance, and this is exactly what I wanted
Is there debian based immutable distro?
Yes, it’s called VanillaOS! vanillaos.org
Thank you)
Isn’t it based on Ubuntu?
I think it was prior to version 2, but these days it’s based on Sid - vanillaos.org/nerd-info
Good. I just quickly glanced at the site and there were multiple mentions of Ubuntu… Glad they switched to Debian, this way I might try it on second PC.
Could you share some pics (without anything private ofc) of bazzite? I wanted to try it but I couldn’t use it as live distro. My main problem is arch because I’m used to
aptand I find pacman or whatever it uses difficult for me (nothing I can’t learn ofc)What do you mean? Thanks
Isn’t bazzite fedora-based? Meaning you use
dnfinstead ofaptorpacman.I don’t know what it uses and as someone who always used apt, pacman or dnf is hard to understand
Edit: Not that I can’t learn… Just saying is hard for me
Since it’s immutable, you’ll probably not be using DNF much.
Good point!
I use Aurora Linux which is the sister one to Bazzite, both are Fedora 41 based images. They strongly encourage using the FlatPak approach to installing software. After using it for a few weeks now, I can see why. One of the things with the immutable setup is once you install a program, you have to reboot to get it to run, but with Flatpak, it isn’t so. I think Flatpak has it’s merits - if they have an app which you normally use, then it’s easy enough to install and go.
For the Fedora side of things, you can “layer” apps over it using the rpm-ostree but they encourage you to only do that as a last resort. One of the things they enable you to do is install additional OS’s containerized which integrate with the desktop environment. For example, right now, I can only run Scrcpy in a different OS (That I’ve been able to figure out so far), so I just spin up an Arch OS container and launch it from there, and can interface with my phone normally. As I understand too, the developers plan on disabling layering in a future release. To be honest, I don’t think I have but one thing layered and that’s my Label Printer’s driver.
The benefit for me using the immutable system and this is the hardest thing to grasp for a lot of people including myself is that it truly is set and forget type of updating. With Arch, you can become sort of addicted to checking for new releases, and I’m not going to lie, it’s amazing to get some of the newest releases of your favorite app or browser especially when they fix something. With Arch, it’s generally there. With my system, I turned on auto updates, so it’s not too uncommon to bring the system up in the morning and see that updates have been given (I don’t notice them usually). It’s nice not having to worry about that as much.
Is it stable enough to recommend for non-techy users? Set-and-forget sounds ideal for someone who doesn’t understand (and doesn’t really need to understand) all the updates their machine is doing.
In my opinion so far yes, I’ve only been on it a few weeks, but think of the immutable as locking down the root partition and any vital directories to the OS and not allowing your user to modify anything. In the event of a bad update, it’s easy enough to select the previous boot in Grub and be on your merry way.
I have a special needs adult step-daughter who’s PC I manage and I always need to keep it updated, setting it up on their Bluefin version which uses Gnome which she loves. So, I may do it this weekend. She’s currently on Endeavor OS (Arch based) but it keeps getting kernel updates daily it seems and with those a reboot. Additionally, for whatever reason, her system goes to sleep without warning sometimes so if I’m updating it, it’s gone to sleep. (Super weird). I’ve never had it do this before with Standard Arch linux so I think its something to do with Endeaver. I’ve never bothered to troubleshoot it to be honest. With a setup on the BlueFin (Aurora Linux is KDE), enabling Auto updates should be a breeze and then she’s golden for being updated without my intervention.
Thanks, I’ll keep an eye on the projects and maybe switch at some point
Bazzite comes packaged with the essentials so that anyone can use it without using terminal. Flatpak is enabled by default and this is the best approach. You can check it out below.
docs.bazzite.gg/Installing_and_Managing_Software/
If you’re not comfortable yet using any other terminal package manager other than apt, you can still use bazzite and learn with time. You can install most apps through Discover (KDE) or Gnome software
I don’t have any pics cause I’m not currently near my computer that runs bazzite.
If you’re mainly using GUI apps you’ll probably just be installing everything through flatpak, which you can use via the Discover store that comes with KDE Plasma. CLI apps are installed using homebrew.
The docs might give you some insight on using it: docs.bazzite.gg
Noooooo! I’ll install it on VM
99% of the times on KDE neon I install using deb files and dpkg
So, you’re saying that immutable is terrible for system uptime.
Uptime is for services, not individual servers.
You have to reboot machines to run secure kernel code. High uptime means running outdated, vulnerable system code.
I heard both flatpak and immutability are obstacles to developers. How bad is it really?
I’ve had NixOS absolutely refuse to run some compiler toolchain I depended upon that should’ve been dead simple on other distros, I’m really hesitant to try anything that tries to be too different anymore.
It would be a problem without distrobox. Since that gives you a normal, mutable OS on top, you don’t even notice the immutability.
And Homebrew. I’m a developer and I’ve done all my work just with Homebrew.
if you program using vscodium, do you install a separate vscodium in every distrobox?
Yep, I do currently. I only have one main distrobox.
I had a lot of issues on silverblue using vscodium as a flatpak, I think I will try installing it in a distrobox instead.
It should behave pretty much the same as a normally installed version. Hope it works well for you!
Yes, some toolchain expect you to run pre-compiled dynamically linked binaries. These won’t work on NixOS, you need to either find a way to install the binary from nix and force the toolchain to use it or run
patchelfon it somehow.Or enabling nix-ld can often get such binaries working.
NixOS likely only refused to run it because you weren’t running it in the Nix way. That’s not a jab or anything, Nix has a huge learning curve and requires doing a lot differently. You’re supposed to use devshells whenever doing development. If you want something to just work, you use a container.
Whatever issue you ran into most likely had nothing to do with NixOS being immutable, and was probably caused by the non standard filesystem hierarchy, which prevents random dynamically linked binaries from running.
I’ve never heard of flatpak and immutability being obstacles to developers, in fact I generally hear the opposite. Bluefin is primarily targeted at developers, and some apps, like Bottles, will only officially support the flatpak distribution because of the simplicity and benefits it brings over standard distro packaging.
Same issue, I still use nix on m’y laptop because it’s neat as can be, but I have to admit developing on nix can be quite a hassle if you don’t go it “the nix way”, moreover some packages don’t work as well because nix doesn’t link binaries the standard way (zed editor for example)
I am a huge fan of immutable distributions, not for my personal daily driver but for secondary systems like my living room/home theater PC.
I have investigated the idea and came to the conclusion that immutable distros are essentially a research project. They attempt to advance the state-of-art a slight bit but the cost is currently too great.
Perhaps somebody will some day create something that’s worth switching to. But I don’t think that has happened yet, or is happening with any of the current distros. Silverblue might become that with enough polish, but I feel that to get that amount of polish, they would have to make Silverblue the 1st class citizen, i.e. the default install of Fedora.
I don’t mind flatpaks in a pinch, but having to use them for literally every app on my computer is an unreasonable amount of bloat.
But the more apps the more the dedup is saving space
Not when every app decides to use a different point version of the same damn platform.
"Hello Mr. Application. I see you’d like to use the Freedesktop-SDK 23.08.27
“Oh…well hello other application. What’s this? You want to use Freedesktop-SDK 24.08.10? Well…I guess so…”
Edited to add: Yes, I know that flatpaks will upgrade to use updated platforms. But it doesn’t automatically remove the old one, forcing you to have to run flatpak remove --unused every week just to keep your drive clean. That’s hardly user friendly for the average person.
The average person has a 1tb+ drive and doesn’t care about a few hundred megabytes of bloat in a partition they will never look at. If someone is switching from Windows, every app having its dependencies self contained is mostly normal anyway (aside from the occasional system provided dll). The only people likely to care about removing old flatpak platforms are the kind of people who don’t mind running the command to remove them.
That’s a very fair point. But it’s still annoying.
The average person definitely doesn’t have a 1tb drive.
61% of steam users have 1tb or more total hard drive space.
…steampowered.com/…/Steam-Hardware-Software-Surve…
I don’t think Steam users really represent the average person…
The average person doesn’t own a computer anymore, but I think steam users are pretty representative of people who want to use the OS that markets itself as “The next generation of Linux gaming”
Steam users are not the “average user”… they are the “average gamer”.
The average person has a phone, with 128gb of storage.
The typical laptop I deal with have 512gb ssd drives.
The typical desktop in a corporate environment is 256gb or 512gb.
1tb drives are very much not “average”.
I had a systemd unit that ran it weekly after the update one ran. I feel like the default behavior though should be automatic purge old unused runtimes though too. I don’t see why that wouldn’t the case to me.
I’ve even gone so far as wanting to force run time changes underneath the packs because of Caves and such, but thats my niche and puts security over function.
Definitely not a free lunch sys admin wise, but it is still a marked improvement over native apps 98% of the time for me.
The barrier for me is that I use a lot of apps which require native messaging for inter-program communication (keepass browser, citation managers talking to Libreoffice, etc.), and the portal hasn’t been implemented yet. Its been stuck in PR comment hell for years. Looks like its getting close, but flatpak-only is a hard no go for me until then.
Even after that, I would worry about doing some Dev work on atomic distros, and I worry about running into other hard barriers in the future.
Bazzite is great. I was using Nobara before it, and Solus before that and Bazzite has been the best experience I ever had on Linux, I don’t plan on changing distros as long as it remains a thing.
I’m much more comfortable trying things that I’m not sure will (or expect not to) work. I can just blast the toolbox or whatever afterwards.
Compare to some of my earlier forays into Linux, where I’d do some nonsense and then attempts to remove said nonsense would break some other load-bearing part of the OS.
Then you have NixOS, which is declarative, and fairly immutable.
You don’t have to reboot to make changes, but you can’t just run unlinked binaries either.
You can’t do things like edit your hosts table or modify the FS for cron jobs. The application store is unwritable, but you can sync new apps into it .
You have to make changes to the config file and run a rebuild as root.
just for clarity: you can modify stuff like hosts or cron jobs but it’d get overwritten iirc? you can also make the change in the config and have it persist (reproducibility being the main point, not disallowing you to edit your files)
No, that file is located in the nix store and linked back, If you become root and try to edit /etc/hosts It will complain that you cannot edit the linked file.
If you go and try to edit the store directly you will meet the same kind of dead ends because /nix/store is a ro bind mount
With enough root access, time and persistence you could eventually unwrap its flavor of immutability which is why I said mostly immutable. Compared to most operating systems where you can just slip a quick edit into a cron job it’s leagues ahead.
TIL
guess i just never botheres to try cos config change & rebuild wasn’t much more of a hassle :shrugs:
Yep, it is ribbed for your protection. :)
I don’t work in tech but I love to tinker , have a home lab etc. I love using Linux for this, been on Linux for close to 20 years.
Got a steam deck little over a year ago, it was my first immutable
I just moved to an immutable silver blue. Been loving it so far. There’s a few things I have issues with, but it’s “just works”. I still distro hop and fuck around breaking my system for fun from time to time, hahahah. But having my main system on immutable has been great.
I have a really hard time getting Aurora working the way all my other Linux devices so that are running some form of Ubuntu (Mate or Bodhi). With that said, it’s been very stable and i like not being interrupted with packages to install while working on things…
Mixed bag review. I give it 3.5 out of 5 stars.
The whole point of Linux is to tinker, immutable distros destroy the whole point, not to mention, it’s a very windows-approach
Not to mention there’s no guarantee if security even with Immutable distros
Not to tinker is a good thing for me at least. Some are Ok using LFS, Gentoo, etc. But distribution like Fedora Silverblue is low maintenance as i just want my task easy and an OS that just works.
To You, that’s the keyword here
I don’t think the point of Linux is to tinker. That would kinda make it for tinkerers only. In my view, the point of Linux is that its a kernel only and you can use it to build an OS around and build one which is easy to tinker with or one which isn’t. Point is, not every system is suited for every task and the Linux kernel allows you to use it how you wish (via distros or you can make your own system around it). Why the gatekeeping?
It is, it’s your machine, it’s YOURS to tinker to your needs
Or yours to not tinker and just use distros default. Right?
Umm sure, mutable ones give you the freedom
How does immitable differ in this case?
Cuz it’s immutable
When I just want it to work for my needs (i.e. using just web browser for most people) there’s no difference. Except immutable is less prone to go wrong.
The whole point of Linux is to be a FOSS kernel/OS, that’s it.
Anything you want to (legally and morally) do with it is fine and you should not have to conform to arbitrary limitations set by others.
If you think that Linux is only for tinkering, not only are you completely wrong (since most machines running Linux are meant to be stable and not tinkered with, think servers, iot, embedded devices, etc) you are also missing the point of FOSS, since it aims to give the user freedom to do as they see fit, which includes preferring stability and security over tinkering.
There’s Linux-Libre
Fair enough but the sole reason I went to Linux is because I despise Microsoft. I wanted a less bloated, not ad ridden, and more customized( mainly just the GUI) experience that gave me more control over my PC. Now I only use this PC for gaming and streaming, so really I just want those two things to work with as little fiddling as possible. Obviously everyone’s use case is different and immutable is definitely not a good choice for power users (from what I’ve read).
Everyone has their own opinion, personally I think they’re a great idea and have lots of great applications. But just like rolling vs non-rolling release it’s a personal and application dependant choice.
Again, depends, for my personal computer I wouldn’t use it because I think it could get complicated to get specific things to work, but for closed hardware like the Deck or even a fairly stable desktop used as a gaming system it’s perfect.
It could, it can also hamper it because people might start to try solutions that only work until next boot and not understanding why, or having problems getting some special hardware to work (more than it would be a mutable distro). But there is a great counter to this which is that once it’s running it will be very difficult to break by user error.
At the end of the day I think it’s a cool technology but that people should know what they’re getting into, just like when choosing rolling vs non-rolling distro, it’s not about what’s better, but what suits your needs best.
From an advertising perspective, it’s important to think about who you’re targeting. Who are your likely customers? Certainly there are some based on the strengths that you raised.
However, some people are definitely not a good target audience, and some people is actually a very large group of people. There are a lot of current and potential users who essentially want the standard major applications to work, and they’re not going to touch the root partition, and they want things to be very simple. For people like that, Debian or Ubuntu or Fedora already do what they want. And these major operating systems have been around for so long that people will naturally be more confident using them, because they were their friends have experience, or because they think the organization has more stability because of its experience.
Of course a lot of things depend on how you define words, but to me the above paragraph describes the mainstream audience, and I don’t think you’re going to have much luck reaching them, because I don’t think the thing you’re trying to sell gives them extra value. In other words, it’s not solving a problem for them, so why should they care.
Since the idea is that the “root partition” is immutable, serious question:
How do you fix a hardware config issue or a distro packaging / provision issue in an immutable distro?
Several times in my Linux history I’ve found that, for example, I need to remove package-provided files from the ALSA files in
/usr/share/alsain order for the setup to work with my particular chipset (which has a hardware bug). Other times, I’ve found that even if I set up a custom.XComposefile in my $HOME, some applications insist on reading the Compose files in/usr/share/X11/localeinstead, which means I need to be able to edit or remove those files. In order to add custom themes, I need to be able to add them to/usr/share/{icons,themes}, since replicating those themes for each $HOME in the system is a notorious waste of space and not all applications seem to respect/usr/local/share. Etc.Unless I’m mistaken on how immutable systems work, I’m not sure immutable systems are really useful to someone who actually wants to or needs to power user Linux, or customize past the “branding locking” that environments like Gnome have been aiming for for like a decade.
My guess would be: have an additional overlay filesystem on top of your immutable root and apply all your fixes to it.
On the one hand sounds sensible, on the other hand I wonder if that’s possible when wanting to apply things that need to take place as early in boot as possible (eg.: modprobe options for a module, apparmor profiles, …).
turn off. immutable